Artificial intelligence has transformed the way we search, work, and even consume. New developments keep coming, tools are evolving rapidly and becoming increasingly “intelligent.” The promises are numerous: time savings, increased productivity, cost reduction… but between the promises, sometimes excessive enthusiasm, and the reality on the ground, it’s not always easy to navigate. Here, we offer a clear definition of autonomous agents to help you understand what they are, what they can do, and form your own opinion.
What is an autonomous agent?
An autonomous agent is a software program that uses artificial intelligence to interact with its environment, make decisions, and act autonomously, according to predefined objectives. The goal of an autonomous agent is to operate without human intervention while acting in the best interests of its owner.
Also known as AI agents, these systems can range from simple programs driven by fixed rules to much more advanced solutions capable of adaptation and reasoning. These agents can therefore be seen as simple assistants for performing repetitive tasks, or as real solutions for imitating human behavior, or even performing tasks that a human could not handle alone due to lack of time, data, or processing capacity.
Autonomous agents vs. traditional software
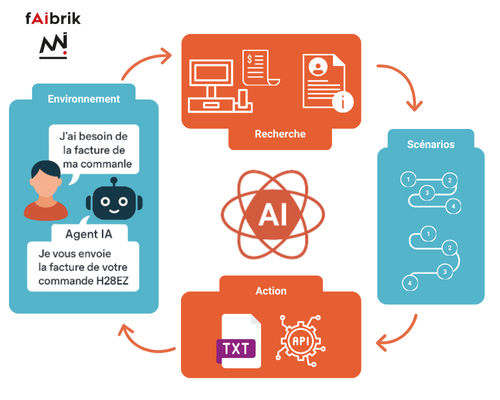
What distinguishes autonomous agents from other, more traditional software programs is their ability to make rational decisions based on their environment to achieve a specific goal. This environment can include internal knowledge bases (documents, business data, connected tools), but also public sources such as web pages, FAQs, or online documentation.
In concrete terms, the agent interacts with its environment, considers all possible scenarios to achieve its goal and analyzes them, then creates a sequence of tasks to achieve this goal. It then defines the steps to follow and executes them, adapting if some don’t work as expected.
What makes it 100% autonomous is the fact that it doesn’t require a human-defined action plan to perform these tasks. The agent can handle the unexpected on its own, without the need to anticipate all possible conditions from the outset.
You may have already used it without realizing it. Indeed, on tools like ChatGpt, Perplexity, or Gemini, some in-depth searches are handled by autonomous agents. These agents break down your question, analyze its meaning, explore multiple sources, and then synthesize an answer as precise as possible. This explains why some answers take a little longer to arrive.
These agents overcome some of the limitations of traditional software, which follows predictable, fixed scenarios without the ability to adapt in real time.
Multi-agent systems
An autonomous agent can also collaborate with other autonomous agents to achieve a common goal. Each agent has its own specific role and area of expertise to accomplish its mission. Thus, a true artificial intelligence organization is formed within the company. At fAIbrik, we implemented such a system for one of our clients by combining two agents. The first generates content, while the second corrects and optimizes it. The two agents interact until all the criteria defined by the client are validated.
The role of autonomous agents in customer service
Customer service has become a key pillar for businesses, and artificial intelligence naturally finds its place within it. It already makes it possible to analyze, prioritize, and assign requests, while significantly reducing response times. However, if poorly configured, it can lack nuance, empathy, or efficiency in ticket resolution. Customer expectations are increasingly high and demanding, forcing businesses to adapt to new standards. According to Accenture’s latest customer service study, 35% of respondents said they feared AI would further degrade the quality of customer service in the coming years.
It is in this context that autonomous agents are generating interest. Their functioning is similar to that of a human: they analyze, reflect, and undertake appropriate tasks. For example, in a conversation related to a customer service issue, the agent can understand the request, act to satisfy the customer, and adapt to unforeseen situations, all while maintaining a consistent and empathetic tone.
These agents can intervene in both pre-sales and post-sales support. They can take the initiative in pre-sales to suggest products based on customer preferences or propose service improvements. In post-sales support, they are able to identify a customer’s problem and offer appropriate solutions to ensure customer satisfaction.
Survey on the use of AI by companies
fAIbrik and CitizenCall are partnering to better understand how companies are using AI agents in their customer service. Take our survey and receive our exclusive white paper on AI practices and trends in business to improve the customer experience.
To do this, we need your participation in a questionnaire for companies with customer service, whether in-house or outsourced.
Don’t miss this opportunity to contribute and discover best practices for AI in customer service!
